Set up AI agents for customer support in less than 10 minutes
Set up AI agents in minutes
How to handle customer requests: A step-by-step guide for support teams
Vaishali Jayaprakash .
Aug 2025 .

A surprising fact - 88% of customers expect a response within 60 minutes.
Your response time isn't just another metric. It often determines whether customers pick you or your competition. Every customer question matters, but responding to all of them right away isn't possible.
The consequences are serious. Negative reviews keep an average of 40% of shoppers from buying from a company. Revenue-critical requests need the highest priority level.
Quality customer support makes a real difference to business success. The challenge lies in balancing speed with quality as requests pour in.
Customer needs must be prioritized properly. A prioritization framework helps make decisions consistently. This ensures you handle the most urgent customer requests first while managing everything else within reasonable time.
This piece lays out a step-by-step process to handle customer requests the right way. You'll learn everything from categorizing incoming problems to picking the right tools and making your system better over time.
Understand the nature of customer requests
Customer queries that land in your inbox are unique, yet they follow recognizable patterns. These patterns are the foundations of customer request management that works.
Types of customer service requests
Customer service requests usually fall into three basic categories:
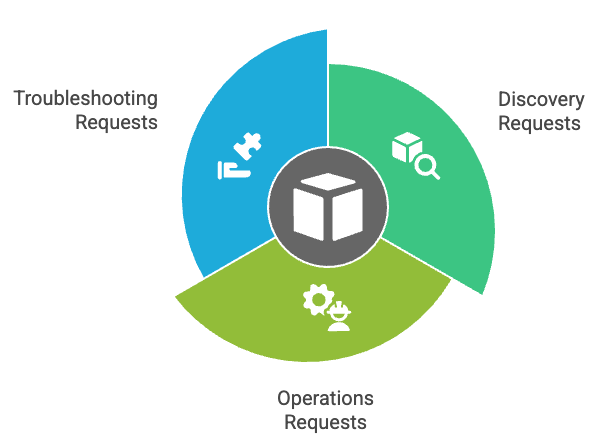
- Discovery requests: These are questions where customers ask to understand your product or service better. To cite an instance, customers might ask about features, pricing plans, or integration capabilities. Potential customers who assess your offering often send these requests.
- Operations requests: These involve administrative tasks customers need you to perform. This includes processing refunds, changing shipping addresses, or updating account details. These requests need careful handling because they deal with financial transactions or personal data.
- Troubleshooting requests: Something isn't working as expected in these cases. They need diagnosis and are often unpredictable. The biggest problem lies in finding the root cause since customers usually report symptoms rather than causes.
Support teams of all sizes now handle questions through multiple channels like phone, email, live chat, social media, and self-service portals.
Why not all requests are equal
Customer service teams can't treat all requests equally. Some need immediate attention while others can wait. Smart support teams don't use first-come-first-serve. They set priorities based on several factors.
Time sensitivity comes first. Order-related questions need faster responses than general feedback. The channel matters too—customers who use chat expect quicker responses than email users.
Pre-sales questions deserve top priority. Your support team could make or break that sale.
Many teams use this tiered system to set priorities:
- Low priority: Non-urgent questions that don't stop product use
- Medium priority: Problems that don't completely block service
- High priority: Issues that substantially affect functionality
- Critical priority: Problems that stop product use entirely
The role of urgency and impact
A request's priority level depends on two vital factors: urgency and impact.
Impact shows how an incident affects business processes and service quality. Teams assess this by looking at the number of affected customers, potential revenue loss, or systems involved.
Urgency shows how quickly an incident will hurt your business if left unaddressed. A high-impact issue might not be urgent if its effects show up later.
Looking at both factors creates a priority matrix that guides response times. A request with wide impact and critical urgency gets the highest priority (level "1") and needs immediate attention.
This organized approach helps critical issues get quick attention while keeping reasonable response times for less urgent matters. Your team can focus their efforts where they'll help most and balance customer satisfaction with operational efficiency.
Set up a prioritization framework
Your team needs a clear way to handle different types of customer requests. A well-laid-out system will help them decide which requests need attention first.
Using a priority matrix
The quickest way to figure out how important each customer request is, by using a priority matrix. This matrix looks at two main things: the effect and how urgent something is. Your support team can use this to make better decisions than just handling requests in order.
The matrix works as a grid with impact on one side and urgency on the other. Here's what it looks like:
Impact/Urgency | Low | Medium | High | Immediate |
Small | P5 | P4 | P3 | P3 |
Minor | P4 | P3 | P3 | P2 |
Major | P3 | P3 | P2 | P1 |
Critical | P3 | P2 | P1 | P1 |
P1 means highest priority (handle right away) and P5 means lowest (can wait). The team can see at a glance how to rank new requests.
Defining impact and urgency levels
The impact shows how much an incident disrupts business operations. Your team should look at these factors to determine impact:
- Number of people or customers affected
- Amount of lost revenue or incurred costs
- Number of systems/services involved
Most companies use four levels of impact:
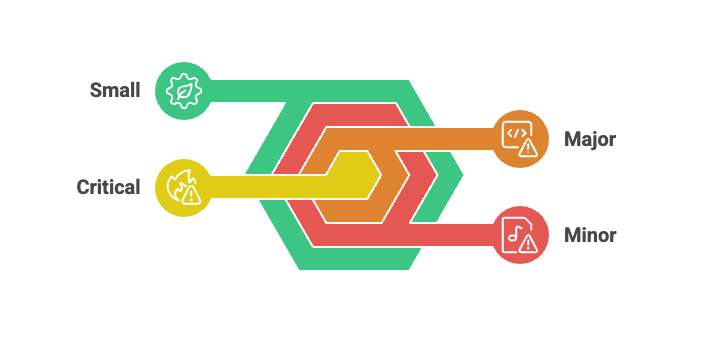
These labels help everyone understand things the same way.
Urgency focuses on time - specifically how fast someone needs an answer. Something might have a big effect but low urgency if the problems won't show up until later.
The standard urgency levels are:
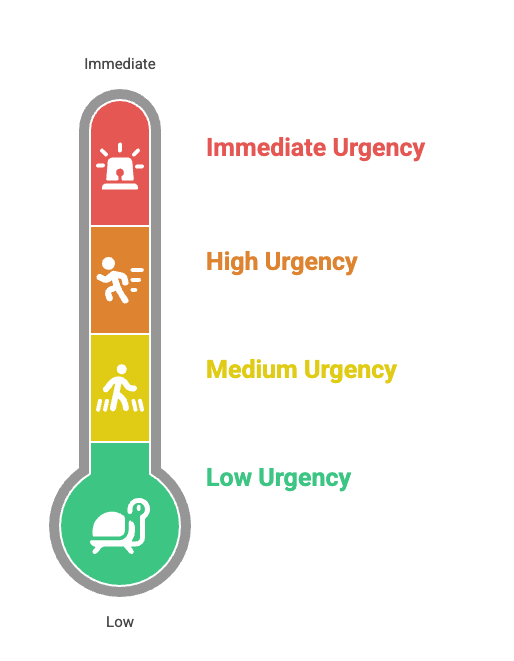
Each company sets these based on their situation and risks.
Clear written definitions with examples will help your team apply these levels consistently.
Creating customer tiers for prioritization
Customer segments add another layer to prioritization. This recognizes that some customers matter more strategically to your business.
You can tier customers these ways:
- Value-based segmentation: Give priority to regular buyers or longtime customers when issues are equally urgent.
- Strategic importance: Add "VIP" tags for key accounts and watch their requests separately.
- Service level agreements: Set different response times based on customer level.
A good tiering system looks at multiple factors. You might sort by urgency first, then use customer tier within each urgency group.
Note that while customer level matters, truly urgent issues come first. A critical problem affecting your product needs immediate attention whatever the customer's tier.
Using both a priority matrix and customer tiers creates a resilient framework that balances urgent needs with key business relationships. Writing down these guidelines will help your entire support team apply them consistently.
Implement a step-by-step prioritization process
Your team needs a systematic approach to put this prioritization framework into action. A well-laid-out process will give your support team consistency and create better customer experiences.
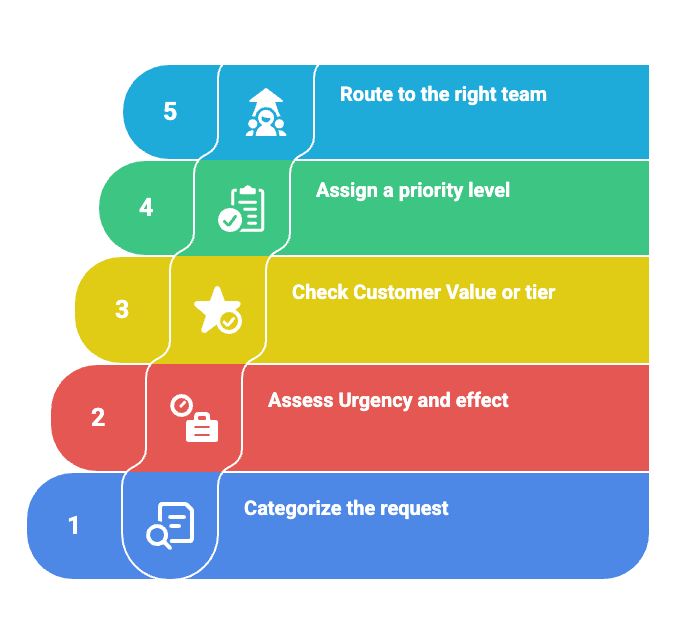
Step 1: Categorize the request
Start by figuring out the type of request you have. Good categorization helps send issues to the right teams and builds a solid base to prioritize work. You can sort requests by:
- Nature of the request: Technical issues, feature requests, complaints, or information inquiries
- Department: Billing support, technical support, or account management
- Product area: Which specific product or feature it affects
Support teams often use keywords in ticket content to automatically sort incoming requests. Keywords like "incorrect bill" or "invoice" can send tickets straight to your billing team.
Step 2: Assess urgency and effect
Look at both urgency and effect factors:
To measure urgency, ask:
- Is this time-sensitive?
- Could the problem get worse quickly?
- Do we have a workaround?
To measure effect, check:
- How many customers/users it affects
- Revenue loss or extra costs
- Systems or services involved
Note that high effect doesn't always mean high urgency. A system-wide issue might be serious but not urgent if it won't hurt the business right away.
Step 3: Check customer value or tier
After the technical review, look at the customer's status:
- Are they a high-value customer?
- What's their history with your company?
- Do they have specific SLAs (Service Level Agreements)?
Customer tiers help balance business priorities with fair treatment. Revenue matters, but a critical issue that stops any customer from using your product needs immediate attention, whatever their tier.
Step 4: Assign a priority level
Mix all these factors to set a clear priority level. Most companies use a simple 1-5 or 1-4 scale where 1 is highest priority:
- Priority 1 (Critical): Core system down; users in multiple sites can't access system; needs immediate response
- Priority 2 (High): Main function fails without workaround; needs response within hours
- Priority 3 (Medium): Issue has workaround; can wait 1-2 business days
- Priority 4 (Low): Minor or cosmetic problem; can schedule within several days
Your urgency-effect matrix helps place each request on this scale.
Step 5: Route to the right team
Send the request to the right team or person based on:
- Request category
- Required expertise
- Current workload and availability
Smart routing systems can match agent skills, workload, and availability to find the best customer service representative. This cuts out manual sorting, reduces burnout, and lets your team tackle high-impact work.
Bigger organizations should set up escalation rules to handle issues quickly if they miss target response times.
Use tools and automation to streamline requests
Technology powers modern customer request management. The right tools reshape how support teams handle incoming tickets and make the prioritization frameworks we discussed earlier work effectively.
Benefits of AI in customer requests management
AI has become vital for customer service, not just another upgrade option. Support teams that use AI see 17% higher customer satisfaction scores.
This technology brings clear advantages:
- Automated categorization and routing – AI systems analyze incoming requests and direct them to appropriate teams based on agent skills and expertise, not just availability. This skill-based routing connects tickets with agents who can resolve them quickly.
- Reduced response times – AI-powered chatbots handle simple questions immediately and provide 24/7 support without human intervention. Wait times decrease while agents focus on complex issues.
- First-contact resolution – Smart ticketing systems automatically categorize, prioritize, and route tickets to the right agent. This improves the chances of resolution during first contact.
Setting up automated rules and triggers
Automation setup needs careful configuration. The first step identifies repetitive tasks that take up agent time—ticket creation, routing, or status updates work well for automation.
Rules that trigger specific actions based on predefined conditions come next. These conditions might include ticket source, status changes, priority changes, or language. Actions can range from setting assignments to sending messages or changing status.
The best approach tests one function first (like an email autoresponder) and measures results before expanding. This helps show value to leadership while making sure systems work correctly.
Tracking SLAs and response times
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) set response time expectations and work as vital accountability tools. Good SLA tracking lets you:
- Monitor performance against targets
- Set up automatic alerts for potential breaches
- Escalate issues before deadlines pass
Advanced SLA management tools let you customize work schedules so SLAs apply only during business hours. Your team's performance gets measured fairly and customers know exactly when to expect responses.
SLA metric tracking also helps optimize support operations. Response times, resolution rates, and achievement percentages against targets stand out as customer service KPIs to watch.
Refine Your System with Feedback and Data
Your prioritization system needs regular refinement to work well. The next vital phase comes after implementing your framework and tools. You must analyze performance data and make informed adjustments.
Monitoring customer satisfaction
Customer satisfaction directly affects loyalty and retention. Companies that monitor quality metrics through statistical process control report defect reductions of up to 40%.
These improvements lead to higher customer satisfaction scores. Here's how to track satisfaction effectively:
Multi-channel feedback collection should span across all touchpoints. Text messages achieve a remarkable 98% open rate compared to email surveys. This higher response rate produces more accurate customer support metrics. Your team gets a complete view of sentiment throughout the customer's experience.
Key performance indicators include response times, resolution rates, and customer satisfaction scores. Your customer service software helps monitor these metrics to ensure positive trends. Declining numbers often point to needed process changes or additional training.
Note that 94% of customers say a positive service experience makes them more likely to purchase again. Measuring satisfaction isn't just about procedure—it directly boosts revenue.
Adjusting priority rules based on trends
Historical data helps refine your prioritization framework. This method offers one big advantage: you already have the data. Look for patterns in:
- Issue types and frequency – Study which categories create the most tickets and check if they match your current priority settings. To name just one example, if data shows "missing item" complaints strongly relate to customer churn, your rules should prioritize these tickets.
- Customer sentiment trends – Negative sentiment often signals potential churn, refunds, or negative word-of-mouth. Analysis typically shows angry sentiment related to repetitive issues. These insights should shape your prioritization rules.
- Reassignment patterns – Tasks with few reassignments might work well with automation through workflows or virtual agents. Your team can then focus on complex issues that need human judgment.
Training support teams for better judgment
Human judgment remains essential despite advanced tools. Training should emphasize:
- Detail orientation – Careful tracking of conversation details offers clues toward appropriate solutions. Teams should review cases with missed details and learn to spot them.
- Data interpretation skills – Teams need to understand trends and historical response patterns. This knowledge helps agents make better up-to-the-minute prioritization decisions instead of blindly following rules.
- Customer tier recognition – Agents must understand different customer segments' strategic value while ensuring critical issues get immediate attention whatever the customer tier.
- Your training initiatives should include regular agent surveys to compare results against your baseline. This feedback ensures your prioritization system keeps improving.
Conclusion
Customer request management is the life-blood of business success. This guide shows how smart prioritization can turn chaotic support queues into smooth workflows. Your team will now know how to sort requests, judge their urgency and effect, and send them to the right specialists.
Quick responses matter to customers - 71% of consumers (aged 16-24) and 65% of consumers (aged 25-34) believe quick responses drastically improve customer experience. A well-laid-out priority system will help meet these expectations while keeping service quality high. The urgency-impact matrix gives your team a reliable way to handle critical issues right away and deal with less urgent ones at the right time.
Smart technology makes this whole process run better. AI tools can sort and route tickets on their own, which cuts down response times and lets your agents focus on tough problems. These systems can track SLAs and spot potential issues before they become real problems.
Note that your priority system must grow and change. Customer feedback and performance numbers will teach you what needs fixing. Keep an eye on satisfaction scores from all channels and tweak your priority rules as new patterns show up. This way, your approach stays strong as customer needs shift.
Without doubt, mixing speed and quality takes both good systems and human smarts. Support teams need the right training to make good choices within your framework. When you combine clear priorities, smart tech use, and constant improvements, you create a customer service operation that builds loyalty, keeps customers around, and helps your business grow.
Quick summary – How to handle customer requests
This guide provides a structured, step-by-step approach for support teams to manage customer requests efficiently while balancing speed and quality. It covers:
- Request Categorization: Identify the type—discovery, operational, or troubleshooting—and route to the right team.
- Prioritization Framework: Use an urgency-impact matrix and customer tiers to rank requests, ensuring critical issues get immediate attention.
- Step-by-Step Process: Categorize → Assess urgency/impact → Check customer value/tier → Assign priority → Route effectively.
- Automation & AI: Leverage AI for ticket categorization, routing, and faster responses, plus automated SLA tracking to prevent breaches.
- Continuous Improvement: Monitor customer satisfaction, analyze data trends, refine rules, and train agents to improve judgment and decision-making.
By combining clear processes, smart tools, and ongoing refinement, support teams can deliver faster resolutions, maintain high service quality, and strengthen customer loyalty.
Frequently Asked Questions
MORE LIKE THIS
Support made easy. So your team can breathe.





![Customer care techniques that actually work: A support manager's guide [2025]](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fstatic.cdn.sparrowdesk.com%2Fsite%2Fpayload%2Fuploads%2F2025%2F08%2FCustomer%20care%20techniques.png&w=3840&q=75)