Set up AI agents for customer support in less than 10 minutes
Set up AI agents in minutes
Why most support ticket lifecycles fail (And how to fix yours)
Vaishali Jayaprakash .
Aug 2025 .
-900x600.png&w=3840&q=90)
Most companies fail at managing their support ticket lifecycle without even knowing it.
The journey from submitting a ticket to finding a solution can be complex. Support teams must know the ticket lifecycle stages to optimize operations and deliver great customer experiences. Customer expectations make this even more important - 66% of consumers expect a response from customer service in five minutes or less.
Broken help desk workflows create problems beyond team frustration. They hurt your company's relationships with customers. Your ticket workflow shows how well your company solves problems, and poor ticketing management affects customer satisfaction directly. Delayed responses from support teams put valuable client relationships at risk. This piece explains why most ticket resolution processes break down and offers practical ways to improve yours.
Where most support ticket lifecycles break down
Support tickets often break down at their most important points. This creates frustration for customers and support teams alike. Most organizations face basic problems that stop tickets from being resolved quickly.
Lack of clear ticket categorization
Poor ticket categorization makes support workflows fail. Organizations that use default settings in their automated ticketing systems face several problems. They get bad classification reports, take longer to solve issues, and send tickets to the wrong support groups. The way tickets are categorized affects three areas:
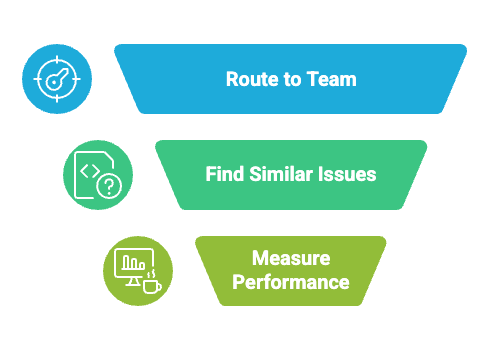
A weak categorization plan causes problems with reports and assignments. This becomes more important as tickets grow from a few each week to thousands every month. Bad classification forces teams to handle tickets in order of arrival. This means urgent issues wait while agents work on older, less important requests.
Delayed or incorrect ticket assignment
Tickets often get stuck when they go to the wrong teams. Wrong classifications cause delays and multiple transfers between teams, which takes longer to fix problems. Users often don't know which category they should pick.
Many companies end up sending tickets to the wrong department or person. New staff members don't feel confident enough to send work to senior technicians, which creates bottlenecks. Having junior staff review and move tickets seems like a good idea. However, this slows things down because new team members don't yet know everyone's strengths.
Poor communication during resolution
Teams struggle most with keeping customers updated. Customers feel ignored when no one sees or acts on updates quickly. This always happens with tickets assigned to people on leave or tickets without an owner.
Support teams focus on new tickets and ignore existing ones. Older tickets sit there and create huge backlogs. Tickets marked "on hold" stop the clock on service agreements. These end up at the bottom of the list where they often get abandoned.
Failure to confirm customer satisfaction
Support teams often skip checking if customers are happy after fixing their issues. Without good satisfaction surveys, you miss feedback that could keep customers from leaving and help improve support. These surveys tell you right away how well your team meets customer expectations.
Companies often fail to check three things:
This creates a dangerous gap in knowledge. Without confirmation, you can't tell if customers were happy or just gave up.
Premature ticket closure
Teams often close tickets before fixing the actual problems. Some systems automatically close tickets when customers stop responding. This makes things simpler but leaves customers unhappy when their problems aren't solved.
Besides automatic closures, tickets get closed too early for other reasons. These include vague responses like "Okay" or "That's fine," pressure to show better numbers, and mistakes in communication. Early closure means more work because customers must either reopen tickets or create new ones for the same problem.
Understanding these breakdown points helps you spot specific ways to improve your support ticket process.
Understanding the full ticket lifecycle
The quickest way to manage tickets requires you to understand each stage of the support ticket lifecycle. Your help desk ticket workflow will improve when you become skilled at the five vital phases every ticket goes through—from creation to closure.
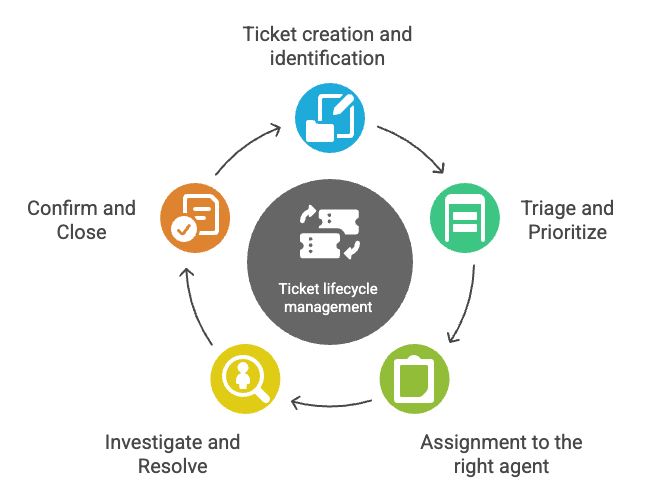
1. Ticket creation and identification
The trip starts when customers submit requests through email, phone, chat, or a self-service portal. The system creates a unique identifier to track each ticket throughout its lifecycle. The ticket gets an automatic "New" status and captures basic details like contact information and issue description. This first stage builds the foundation to manage tickets well by documenting all needed information right from the start.
2. Triage and prioritization
- New tickets move into the vital triage phase where support teams categorize them by issue type and set priority levels. This step needs analysis of the ticket's content to identify severity and determine urgency. Good categorization affects three main areas:
- Correct escalation routing
- Search effectiveness
- Quality of performance reporting
Smart ticketing systems sort tickets by type, category, source, and criticality to set priorities. A good triage system makes sure urgent issues get immediate attention while routine queries wait in line.
3. Assignment to the right agent
After setting priorities, tickets need to reach the right support staff. Teams can assign tickets manually or let automated systems handle it based on set rules. Here are three common ways to assign tickets:
- Round-robin assignment: Shares tickets equally among available agents in rotation to balance workloads
- Load-balanced assignment: Gives tickets based on how busy agents are to prevent overwork
- Skill-based assignment: Sends tickets to agents who have the right expertise
The right assignment cuts down resolution time by matching tickets with agents who have the needed skills and time. To name just one example, tickets in Spanish go to Spanish-speaking agents.
4. Investigation and resolution
The assigned agent breaks down the issue by collecting key information and finding the root cause. Tickets move through different statuses—"Open" when agents work on them, "Pending" while waiting for customer input, or "On-hold" if they need help from others. Good notes about troubleshooting steps help everyone see how the problem gets solved and make future fixes easier. Agents might give instructions, fix technical issues, or ask senior support staff for help.
5. Customer confirmation and closure
The last stage needs you to check if customers are happy with the solution—a step many teams skip but shouldn't. Ask a simple "Does that solve the problem?" before closing any ticket. Customers might find poor workarounds and stay frustrated if you don't confirm the fix. After confirmation, tickets become "Solved" and then "Closed" (usually after waiting a set time with no customer response). Closing tickets properly means writing detailed notes about the solution, which helps teams get better at their jobs over time.
Your support ticket workflow will boost both team output and customer happiness when you get these stages right.
Common mistakes in help desk ticket workflow
Support teams, even those with years of experience, make critical mistakes that hurt their ticket workflow efficiency. You can spot weak points in your own support ticket lifecycle and make targeted improvements by learning these common pitfalls.
Overlooking ticket urgency
Teams often struggle to prioritize tickets correctly. Many use a "first in, first out" approach that leaves urgent tickets waiting while agents handle older, less critical requests. Critical issues like service outages get the same attention as minor questions without clear priority criteria. This happens because:
- Companies don't have systems to prioritize issues based on business effects
- Teams don't evaluate how issues might disrupt business operations
- Priority rules in automation tools fail to flag truly urgent matters
Here's a real scenario: An enterprise customer calls with an urgent request during a major product launch. They wait just as long as a low-priority ticket would—damaging your reputation and putting business at risk.
Inconsistent status updates
Help desk ticket workflow depends on accurate status tracking, yet teams often mismanage statuses. Confusion spreads when agents forget updates or use statuses incorrectly. Too many status options make things worse—your team needs a simpler system if they need a cheat sheet to track statuses.
These status issues create several problems: new technicians take longer to train, automation breaks down as workflows get confused, and reports become useless without complex fixes. Customers looking at these confusing statuses through your portal can't tell how their ticket progresses.
Ignoring follow-ups and escalations
Failed follow-up protocols create another major ticketing management issue. Customer trust breaks down when tickets lack consistent monitoring after the first response. This gets worse with escalations—high-priority issues that need expert attention but lack clear handling rules.
Most organizations don't define clear escalation triggers. This leads to two problems: too many escalations overwhelm expert teams, or too few escalations make customers feel neglected. Teams can't resolve tickets efficiently without structured escalation management, especially when departments work in isolation.
Lack of documentation
Poor documentation stands out as the most common support ticket workflow mistake. This oversight leads to wasted time, repeated work, and unhappy customers. The golden rule of ticketing remains simple but often ignored: "If it isn't in the ticket, it never happened".
Good documentation does more than keep records. A detailed ticket becomes a knowledge base article that helps agents solve similar issues quickly instead of starting from scratch. Clear ticket notes also provide legal protection, accountability, and learning material for new team members.
How to fix your support ticket workflow
Your support ticket workflow needs strategic changes to existing processes. A thorough review of weak points in your current system will help you create solutions that boost efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Automate ticket routing and tagging
Automated ticket routing eliminates manual sorting and cuts down response times. Help desk software can tag tickets with descriptors like "feedback" or "system_crash". These tags provide context and help agents set priorities for each case. Your complex needs might benefit from these approaches:
- Skill-based routing: Tickets go directly to agents with specific expertise, which leads to better first-contact resolution rates
- Workload balancing: Even distribution of tickets among available agents prevents burnout
- AI-powered routing: Content analysis identifies topics and sentiment, so critical issues get immediate attention
Use templates for common issues
Response templates cut down handling time for frequent questions. Your team should create message templates for different channels. Chatbots can handle initial conversations, automated text messages confirm receipt, and email templates address common issues. These saved replies help your team stay consistent while they personalize responses to each customer's situation.
Set up SLA-based workflows
Service Level Agreements (SLAs) set clear expectations for response and resolution times. Your team should define specific criteria for different priority levels. Critical issues might need resolution within 4 hours, while minor requests can take up to 72 hours. Automated workflows triggered by SLA conditions can escalate tickets that approach breach thresholds.
These workflows help agents manage their workload better. Customers also know what to expect from your support team.
Enable internal notes and collaboration
Internal notes create a private communication channel within tickets. Your team can work together without customer visibility. Agents can @mention colleagues to ask for help, share context, or transfer knowledge. This feature becomes valuable when:
- Subject matter experts need to guide without taking over the ticket
- Agents need approval before fixing an issue
- Team members must document sensitive information away from customer view
Train agents on lifecycle best practices
Regular training keeps ticket management principles consistent throughout your organization. New agents should practice with simulated tickets in a safe environment. A buddy system pairs newcomers with experienced agents who review decisions and answer questions.
Your team should stay current on evolving standards through regular training sessions. These sessions cover best practices, new help desk features, and process improvements.
Tools that improve ticketing management
Modern technology provides powerful solutions to boost your support ticket lifecycle from beginning to end. Your team can handle customer questions better and improve satisfaction with the right tools.
AI-powered ticketing systems
AI ticketing systems use advanced algorithms that automate and streamline customer support processes. These intelligent systems automatically categorize tickets, route them to the right agents, and handle many questions on their own. Natural language processing helps understand customer issues with greater accuracy, which reduces misunderstandings and sends tickets to the right people quickly. AI-driven features can solve up to 40% of incoming tickets through automated resolution strategies.
Integrated help desk platforms
Support operations across email, chat, phone, and social media come together in complete ticketing platforms. These systems organize conversations and streamline workflows while giving agents the essential information they need for faster resolving of tickets . Most platforms include customizable workflows that match specific business needs, team collaboration tools, and automation features that handle repetitive tasks.
Real-time dashboards and alerts
Support managers can see critical customer service KPIs like ticket volume, agent workload, and satisfaction scores through intuitive dashboards. These visual interfaces help track performance trends and identify bottlenecks, which leads to informed decisions. Teams can analyze support performance from multiple angles with custom filters, and dynamic charts show how key indicators change over time.
Self-service portals and knowledge bases
Customers can solve issues on their own through self-service options, which reduces ticket volume and boosts satisfaction. Knowledge bases act as central repositories with troubleshooting guides, how-to videos, and FAQs. Customer portals let users submit and track tickets, read knowledge articles, and join community forums. Generative AI tools can spot gaps in self-service content by analyzing common customer questions and automatically create knowledge articles to address these needs.
Conclusion
Support ticket management plays a vital role in delivering great customer service. Poor handling of ticket lifecycles can damage relationships with the customers and slow down team productivity. Solving these issues need careful planning as well as hands-on solutions.
A support ticket system forms the backbone of customer service operations. Smart categorization helps tickets reach the right teams fast. On top of that, clear assignment rules prevent bottlenecks and speed up resolution times.
Good communication matters at every step of the ticket lifecycle. Support teams often struggle because they don't update customers or rush to close tickets. The service quality improves when teams verify customer satisfaction before closing tickets.
Successful support teams use automation wisely. AI-powered routing, custom templates, and SLA-based workflows turn messy ticket handling into smooth processes. Good documentation serves as a knowledge base for future use and stops work from being repeated.
Modern tools can transform your support operations completely. Integrated platforms that bring all communications together and self-service portals that help customers solve problems offer many ways to improve your ticket system.
Note that better ticket workflows do more than just boost efficiency—they build customer loyalty and keep teams motivated. Simple changes in how you handle tickets can lead to happier customers. Look for your biggest challenges first, then add specific solutions to address them. A well-run ticket system doesn't just fix problems—it creates lasting relationships with customers.
Quick summary support ticket lifecycles: Why they fail and how to fix yours
Most companies unknowingly fail at managing support ticket lifecycles, leading to delays, poor communication, and unhappy customers. Since 66% of customers expect near-instant responses, broken workflows can quickly damage trust and relationships.
Where ticket lifecycles break down
- Poor categorization → tickets mislabeled, delayed, or misrouted.
- Wrong assignments → tickets bounce between teams, wasting time.
- Weak communication → customers left waiting without updates.
- No satisfaction checks → teams close tickets without confirming resolution.
- Premature closures → issues marked “resolved” too early, leaving customers frustrated.
The 5 stages of a ticket lifecycle
- Creation & identification – request logged into the system.
- Triage & prioritization – categories and urgency defined.
- Assignment – routed to the right agent/team (round-robin, load-balanced, or skill-based).
- Investigation & resolution – root cause analyzed and fixed.
- Customer confirmation & closure – verify satisfaction before closing.
Common mistakes in help desk workflows
- Ignoring urgency, using “first come, first served.”
- Confusing ticket statuses with no clear updates.
- Weak follow-up and escalation procedures.
- Poor documentation that leads to repeated work.
How to fix your workflow
- Use automation for routing, tagging, and SLA monitoring.
- Create response templates for common issues.
- Apply SLA-based rules to prioritize and escalate.
- Leverage internal notes & collaboration tools.
- Provide ongoing training for consistent lifecycle management.
Tools that help
AI ticketing systems – smart categorization and automated resolution.
- Integrated platforms – unify emails, chats, calls, and social.
- Dashboards & alerts – track metrics and bottlenecks.
- Self-service portals/knowledge bases – reduce ticket volume.
Getting ticket lifecycles right improves both customer satisfaction and team productivity. Automation, strong communication, proper documentation, and modern tools are key. A well-run system goes beyond efficiency—it builds long-term customer trust and loyalty.
Frequently Asked Questions
MORE LIKE THIS
Support made easy. So your team can breathe.



.png&w=3840&q=75)

