Set up AI agents for customer support in less than 10 minutes
Set up AI agents in minutes
Customer service vs customer support: The differences every business should know
Sneha Arunachalam .
Dec 2025 .

Customer service and customer support sound like the same thing, right?
Most people throw these terms around interchangeably. But here's what's interesting: they're actually two different approaches to helping your customers.
The difference between customer service and customer support might seem subtle, but understanding it can dramatically improve your customer retention. And keeping existing customers costs significantly less than finding new ones, so getting this right matters more than you might think.
So what's the real difference between customer service and customer support? How do they work together? And why does getting both right make such a difference for your business growth?
What is the difference between customer service and customer support?
Most businesses have no clue there's actually a difference here. These terms get thrown around like they mean the same thing, but their scope, approach, and focus are actually pretty different.
Customer service: Broad, relationship-oriented support
Customer service encompasses all interactions aimed at enhancing the overall customer journey. It's way bigger than just fixing problems — we're talking about building relationships that last.
Customer service reps help customers through the entire buying process. Before they purchase, during the sale, and long after they've handed over their credit card. Their main job? Making sure customers squeeze every bit of value out of what they bought by answering questions, addressing concerns, and guiding them through various touchpoints.
This is exactly where a platform like SparrowDesk makes life easier. By bringing conversations, context, and customer history into one clean interface, it helps service teams stay proactive, deliver personalized responses, and build stronger relationships without juggling multiple tools.
Support your customers better with SparrowDesk. Start your free trial today.
The Helpdesk your team truly deserves.
Here's what makes customer service tick:
- Proactive approach: These teams spot problems before they happen
- Broader scope: They're involved in the entire customer lifecycle
- Relationship-focused: Building long-term connections beats quick fixes
- Universal relevance: Every business needs this, no matter what industry
- Measured by satisfaction: Success gets tracked through things like CSAT scores
Customer service reps need to know a little about everything — products, services, company policies. But their real superpower? Soft skills that help them connect with people and understand what customers actually need.
Customer support: Technical, product-focused help
Customer support is different. We're talking about fixing specific technical headaches related to your products or services. This is where the troubleshooting experts live.
Support teams jump in when customers can't figure out how to use what they bought or when something breaks. They've got the deep technical know-how to walk people through solutions step by step.
Customer support works like this:
- Reactive nature: Problems happen, then support steps in to fix them
- Technical focus: All about product mechanics and troubleshooting
- Transactional interactions: Clear beginning, middle, and end to each conversation
- Industry specificity: You'll find this mostly in IT, SaaS, and tech companies
- Efficiency metrics: Success means fast resolution times and actually solving problems
Support specialists need serious technical chops. They've got to understand how products work inside and out, plus know how to troubleshoot when things go sideways.
And while technical support will always rely on skilled specialists, the customer support tools they use can make or break the entire experience. That’s where a modern support platform helps. With features like automated ticket routing, real-time collaboration, AI agents that auto resolves tickets, and an AI assistant that understands context, SparrowDesk makes technical troubleshooting smoother for both your team and your customers—without getting in the way of their workflow.
The Helpdesk your team truly deserves.
Why these terms get mixed up
- They both deal with helping customers. Whether it’s solving a problem or creating a great experience, the end goal looks similar from the outside.
- They share the same channels. Email, chat, phone calls — everything flows through the same touchpoints, so people assume the jobs are identical.
- Even the industry can’t agree. Some say customer support is a subset of customer service; others treat them as two totally different functions.
- Google doesn’t help either. Search “customer service” or “customer support” and you’ll often see the same kind of results.
- This confusion leads to real issues. If you don’t recognize that service focuses on the full experience while support handles technical problems, teams end up misaligned — and customers feel the frustration.
Key differences between customer support and customer service
Understanding these distinctions helps you structure your teams effectively. Let's break down the five key areas where these functions actually differ.
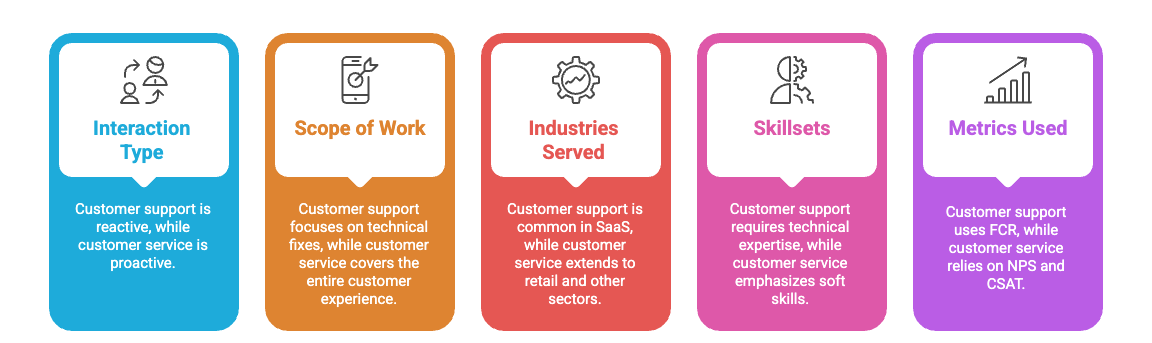
Interaction type: Reactive vs proactive
Customer support typically operates reactively — solving problems that already exist when a consumer reaches out with an issue. Someone emails about a broken feature, and your support team jumps in to fix it. Simple enough.
But customer service takes a different approach. These teams anticipate potential problems and fix them before they happen. For instance, sending maintenance alerts or updating knowledge bases prevents issues rather than just fixing them. It's like the difference between fixing a flat tire and checking your tire pressure regularly to avoid one.
This proactive approach shows customers you care about their experience even before they ask for help.
Scope of work: Technical fixes vs end-to-end experience
Support specialists connect customers to solutions through troubleshooting, technical problem-solving, and finding new answers. Their work has clear boundaries — once the issue is resolved, the interaction concludes. Problem solved, ticket closed.
Customer service covers way more ground. From pre-sale questions to post-purchase satisfaction, service teams assist customers throughout their relationship with your company. They handle general inquiries, offer personalized recommendations, and help with transactions like returns or refunds. This end-to-end approach builds long-term relationships rather than just solving isolated problems.
Industries served: SaaS vs retail and beyond
Not every business needs both functions equally. Customer support positions are most common in SaaS (Software as a Service), e-commerce, and technology industries. These sectors deal with complex products that actually need technical assistance.
Meanwhile, customer service roles exist across almost every industry that serves customers — retail, hospitality, banking, and fast food all rely heavily on service teams. Any business with customer interactions needs service representatives, whereas support specialists are primarily found in technical fields.
Skillsets: Technical expertise vs soft skills
The talents needed for each role are totally different. Customer support requires deeper technical knowledge and hard skills. Representatives must understand product intricacies, troubleshoot effectively, and solve complex problems. According to research from Harvard Business Review, companies focusing on technical expertise ensure accurate solutions.
For customer service, soft skills matter most. Communication, empathy, and adaptability form the foundation for excellent customer interactions. These interpersonal skills help representatives adjust their tone based on customer emotions, ask thoughtful questions, and convey solutions clearly. Companies that focus on emotional intelligence experience a 12% increase in productivity.
Metrics used: FCR vs NPS and CSAT
Even success measurement differs between these functions. Customer support often tracks transactional metrics like First Contact Resolution (FCR), which measures issues resolved in the first interaction. Average resolution time and ticket volume also indicate support effectiveness.
Customer service evaluates broader satisfaction through Net Promoter Score (NPS), which assesses customer loyalty and likelihood to recommend your business. Customer Satisfaction Score (CSAT) and Customer Effort Score (CES) also help gage the overall experience quality.
These different measurement approaches show how customer support aims for efficient problem resolution, while customer service focuses on building lasting relationships and loyalty.
Shared goals and overlapping functions
Despite all their differences, customer service and customer support teams are actually working toward the same thing. Both want happy customers. These overlaps explain why so many people mix up the terms in everyday business conversations.
Customer satisfaction as a common objective
Both functions ultimately aim to create happy customers. Customer satisfaction stands as the primary objective for both service and support teams. According to Zendesk Benchmark data, 73 percent of consumers will switch to a competitor after multiple bad experiences. Even more telling? 3 in 4 consumers will spend more with businesses that provide a good customer experience.
This shared goal makes perfect sense from a business perspective. When organizations delight customers in every interaction, they retain more business. Both functions track similar satisfaction metrics, though with different emphasis:
- CSAT (Customer Satisfaction Score) - Measures immediate reaction to service quality
- NPS (Net Promoter Score) - Reflects the overall relationship with your brand
- CES (Customer Effort Score) - Evaluates how easily customers can get their needs met
Setting clear satisfaction targets helps both teams align with broader business objectives. They can build positive brand reputation, attract new customers, and strengthen market position.
Communication and empathy in both roles
Here's what really matters — effective communication forms the foundation for success in both customer service and support roles. According to the Customer Service Institute, over 70% of customer support interactions succeed or fail based on the representative's communication abilities rather than technical knowledge.
Empathy plays a crucial role across both functions. When representatives acknowledge customers' emotions and respond with understanding, they can diffuse difficult situations. This emotional connection builds trust between customers and companies.
Both roles require representatives to adapt their communication styles to different customer types. As research shows, "it is very beneficial to have different communication styles—it allows you to understand different learning styles and intake styles of information". Representatives must tailor their approach based on individual customer needs.
The ability to truly listen remains vital for both teams. Active listening helps identify underlying issues that customers might not explicitly mention. This skill enables representatives to provide solutions that truly address customer concerns.
Use of omnichannel tools and platforms
Today's customers expect seamless support regardless of which channel they choose. Both customer service and support functions rely on omnichannel platforms that unify interactions across multiple communication channels.
A true omnichannel support platform "unifies every interaction—from email to SMS to social DM—into a single, chronological conversation". This benefits both functions by:
- Eliminating the need for customers to repeat information when switching channels
- Providing representatives with complete context of previous interactions
- Enabling consistent experiences across all touchpoints
These platforms allow teams to move effortlessly between channels while maintaining conversation context. Whether customers start on social media and move to email, or jump from chat to phone, both service and support representatives can access the full interaction history.
According to research, approximately 28% of customers find social media the easiest channel to contact customer service teams. Unified platforms help both functions manage inquiries across these preferred channels while maintaining a consistent brand voice.
The integration capabilities of these customer support tools further enhance both functions. Native integration with CRM systems and other business applications provides representatives with a complete view of the customer relationship, enabling more personalized interactions regardless of whether they're providing service or support.
Roles in the customer journey
Customer service and support don't just randomly show up when customers need help — they each have specific moments when they shine. Understanding when each function kicks in makes all the difference.
Customer Service: Pre-Sale to Post-Sale Engagement
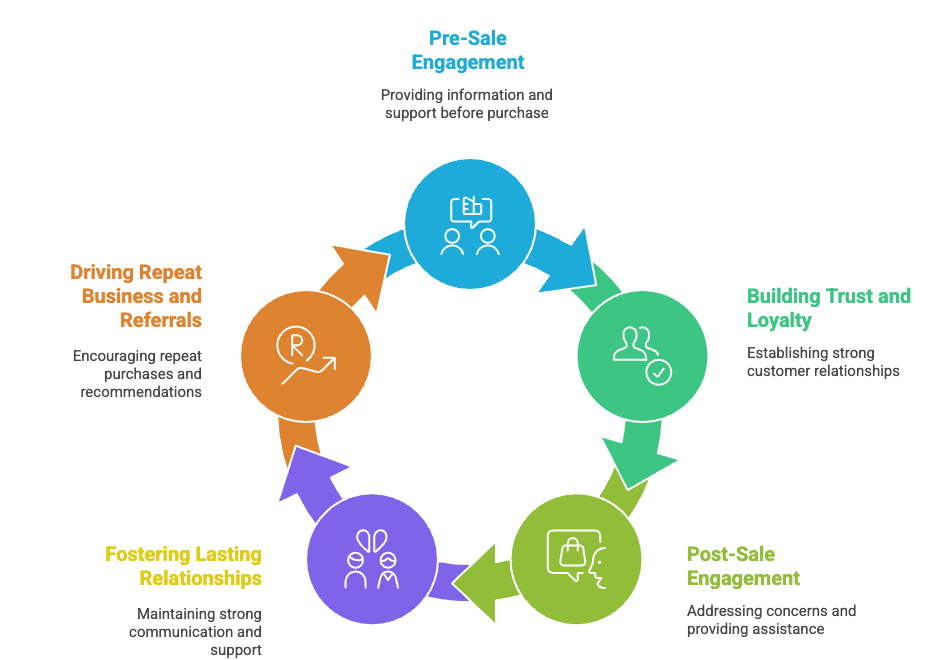
- Customer service begins before the purchase.
Great teams help set clear expectations during sales conversations, building trust early and eliminating frustrating handoffs later. - Smart companies involve service early in the buying process.
This ensures value discussions happen before contracts are signed and lets teams create success plans before onboarding even begins. - Pre-sale service is all about education.
Helping prospects understand the product, guiding them through options, and showing real value before they commit. - After the sale is where customer service shines.
Proactive check-ins, personalized help, and spotting growth opportunities all strengthen the long-term relationship. - Strong customer service drives measurable results.
Forrester reports that companies who truly prioritize customer experience see 28% revenue growth and a 43% jump in customer retention. - This is especially crucial for SaaS.
If customers don’t understand or adopt the product, they won’t stick around — even if the product is great.
Customer Support: Troubleshooting and Technical Resolution
- Support steps in when something breaks.
Unlike customer service, support follows a structured approach: understand the problem, diagnose the root cause, and deliver a clear solution. - Troubleshooting starts with asking the right questions.
Support teams gather context about what customers were trying to do and what went wrong. - They rely on real data to diagnose issues fast.
Logs, product usage insights, and screen sharing help avoid long, frustrating back-and-forth emails. - They isolate the problem.
By removing integrations, add-ons, or custom configurations, support teams can pinpoint the real issue quickly. - Great support simplifies the complex.
Translating technical issues into simple explanations and guiding customers step-by-step is what truly builds confidence. - Speed still matters.
Microsoft’s research shows that 90% of customers expect fast responses when they need help. - Comparing broken vs. working setups helps find root causes.
This approach uncovers small but critical differences that trigger issues.
This entire troubleshooting workflow becomes much smoother with SparrowDesk. Its unified view of customer activity, logs, conversation history, and AI-powered insights helps support teams diagnose faster, explain solutions clearly, and deliver the kind of quick, reliable help customers expect.
Start your free trial today and see SparrowDesk in action
The Helpdesk your team truly deserves.
How both roles contribute to retention
- Both functions directly affect whether customers stay. Even a small 5% boost in retention can increase profits by 25–95% (Bain & Company). It’s not just a support metric — it’s a business survival metric.
- Customer service builds loyalty emotionally.
- Personalized interactions make customers feel genuinely valued.
- Proactive outreach solves problems before they turn into complaints.
- Relationship-building creates trust that goes beyond a single transaction.
- Customer support keeps customers through reliability.
- Smooth, quick technical help prevents frustration.
- Improving First Contact Resolution by 10% can reduce churn by up to 30% (Gartner).
- In SaaS and telecom, unresolved technical issues are among the top reasons customers leave.
- Together, they create a full retention engine.
Forrester calls this the “complete revenue management solution” — because when service + support work together, they guide customers from first interaction to post-sale satisfaction and long-term revenue growth. - Businesses that excel at both thrive.
They create the kind of loyalty that holds strong even in competitive markets, leading to more stable and predictable growth.
Benefits and limitations of each function
"Self-service options can reduce costs while providing immediate solutions to users. Customers have answers at their fingertips, and agents can respond faster, so everyone is happier and more productive." — David Schroeder, Customer service and support technology expert
Both customer service and customer support deliver distinct advantages to businesses. Each function serves unique purposes, yet both come with their own set of challenges.
Customer service: Brand loyalty and personalization
Exceptional customer service directly fuels brand loyalty. When customers consistently receive excellent service, they form a deeper emotional connection with your brand. This relationship building pays off: happy customers are likely to share positive experiences with friends and family, leading to organic growth through word-of-mouth marketing.
Customer service particularly shines in creating personalized experiences. By remembering customer preferences and addressing them by name, service teams show customers they're valued as individuals. This personalization transforms one-time buyers into loyal advocates who actively promote your brand.
The numbers tell the story. Emotionally connected customers provide 306% higher lifetime value and refer others at a 71% rate compared to the average 45%. Besides revenue benefits, devoted customers spend 31% more than new ones and 60% purchase more frequently from brands they prefer.
Customer support: Product reliability and trust
Technical customer support builds confidence through product reliability. When your support team quickly solves technical issues, customers develop trust in both your product and company. In fact, 90% of customers consider a quick response important or very important when they have questions.
Good support drives customer satisfaction. Approximately 90% of customers are likely to return and recommend your business after pleasant experiences with support services. Major organizations like Mayo Clinic, Amazon, Ritz-Carlton, and American Express have demonstrated competitive advantages gained through excellent customer support.
Product reliability creates a virtuous cycle: when customers experience fewer breakdowns and technical issues, their satisfaction increases, leading to stronger brand loyalty. This reliability also improves your company's reputation, which impacts future business opportunities.
Limitations: Resource intensity and skill gaps
Let's be honest — both functions face real resource challenges. Customer service requires sustained relationship-building efforts across multiple touchpoints. This relationship management demands significant time investment, primarily since there's usually no clear endpoint — service teams aim to create ongoing customer relationships.
Customer support faces different headaches. Support representatives need deep product knowledge and troubleshooting abilities, which require extensive training. Finding qualified talent with both technical expertise and communication skills presents ongoing challenges for many organizations.
Both functions struggle with resource intensity — the level of time, effort, and costs needed to perform specific tasks. Organizations that implement proper resource allocation see marked improvements, with companies optimizing allocation models improving customer satisfaction scores by up to 18 percent.
Workload balance remains crucial for both functions. According to a 2025 Gallup study, organizations that actively monitor workload balance report 19 percent higher client satisfaction rates. Preventing burnout protects not only employee well-being but generally safeguards the entire customer experience.
Real-world examples of customer service vs customer support
Sometimes the best way to understand the difference is to see these approaches in action.
Nordstrom's personalized shopping assistance

Nordstrom gets customer service right with their personalized shopping experiences. They offer "Nordstrom To You" styling appointments where a personal stylist helps customers select perfect outfits in the comfort of their home or office. A one-hour styling session costs $50, while a three-hour closet consultation runs $300.
What makes this pure customer service? It's all about building that relationship. They're not fixing a broken product — they're creating an experience that makes customers feel special. And it works. Customers who use personal styling services spend 60% more than those who shop independently.
Apple's remote troubleshooting for iPhones

Apple takes a completely different approach with their technical troubleshooting services. When your iPhone starts acting up, their support specialists walk you through specific solutions to get your device working again.
No relationship-building here — just problem-solving. Their support teams focus on fixing technical glitches, updating software, and making sure everything functions properly. It's all about getting you back up and running as quickly as possible.
Amazon's billing resolution vs microsoft's setup help

Want to see both approaches from the same types of companies? Amazon's billing resolution service is customer service territory. They're handling account issues and payment problems — things that affect your overall experience but aren't technically complex.
Microsoft's setup assistance? That's customer support. They help you configure software or troubleshoot installation problems with step-by-step technical guidance. Pure problem-solving focused on making their product work the way it should.
These examples show exactly how customer service builds relationships while customer support solves technical problems. Both matter, but they're solving different challenges for your customers.
Here's how they stack up: Customer service vs customer support
Dimension | Customer Service | Customer Support |
Primary Mission | Building lasting relationships and enhancing overall customer experience | Resolving technical issues and ensuring product functionality |
Approach Style | Proactive - identifies and prevents potential problems | Reactive - responds when customers encounter difficulties |
Coverage Area | End-to-end customer lifecycle from awareness to advocacy | Specific product-related challenges and troubleshooting |
Core Competencies | Interpersonal skills, emotional intelligence, communication, patience | Technical knowledge, analytical thinking, systematic problem-solving |
When They Engage | Throughout the buying journey - before, during, and after purchase | When products malfunction or users need technical guidance |
Interaction Style | Relationship-driven conversations with no fixed endpoint | Transaction-based exchanges with clear problem-solution closure |
Industry Application | Universal - retail, hospitality, finance, healthcare, every sector | Concentrated in technology, SaaS, IT services, and software companies |
Success Indicators | Net Promoter Score (NPS), Customer Satisfaction (CSAT), loyalty metrics | First Contact Resolution (FCR), ticket resolution speed, fix rates |
Team Positioning | Front-line brand ambassadors across all customer touchpoints | Specialized problem-solvers embedded with product teams |
Communication Channels | Phone, email, chat, social media, in-person, all channels | Primarily digital - help desks, ticketing systems, knowledge bases |
Training Focus | Brand values, conflict resolution, active listening, empathy building | Product architecture, troubleshooting protocols, technical documentation |
Business Impact | Drives repeat purchases, referrals, and long-term revenue growth | Reduces churn through reliable product performance and quick fixes |
Customer Expectation | Feeling valued, heard, and appreciated as individuals | Getting issues resolved quickly and products working properly |
Example Scenarios | Handling returns, answering billing questions, providing recommendations | Fixing software bugs, guiding through setup, diagnosing errors |
Strategic Value | Creates emotional brand connections and competitive differentiation | Builds trust in product quality and company dependability |
Here's the Bottom Line: Customer service vs customer support
Most businesses don't think much about the difference between customer service and customer support until something goes wrong. But once you understand how they work, you start to see opportunities everywhere.
We've covered a lot of ground here. Customer service builds relationships across the entire customer journey — it's proactive, focuses on soft skills, and works in virtually every industry. Customer support tackles technical problems with specialized knowledge, working reactively to solve specific issues when they arise.
But here's what really matters: both functions share the same ultimate goal of keeping your customers happy. They just take different paths to get there.
Think of it like this — your support team makes sure your products actually work, while your service team builds the emotional connections that turn one-time buyers into loyal advocates. You need both.
The stakes are high for getting this right. Remember that 86% of customers leave after just two negative experiences. When you structure your teams with these distinctions in mind, you create an experience that addresses both technical reliability and human connection.
This is exactly where platforms like SparrowDesk shine — bringing service and support under one clean, modern system so teams don’t operate in silos. Agents get the context they need, customers get faster resolutions, and businesses create the kind of consistency that builds trust over time.
Get a 14 day free trial and see SparrowDesk in action
The Helpdesk your team truly deserves.
And that’s what fuels real growth. Because when customers trust your product and feel valued by your team, they don’t just stick around — they become the advocates who drive your business forward for years to come.
Quick summary: Customer service vs customer support
Understanding the distinction between customer service and customer support is crucial for building effective customer experience strategies that drive retention and growth.
• Customer service builds relationships proactively across the entire customer journey, while customer support reactively solves specific technical problems when they arise.
• Different skills drive success in each function - customer service requires soft skills like empathy and communication, while customer support demands technical expertise and product knowledge.
• Both functions share the same ultimate goal of customer satisfaction but measure success differently - service tracks NPS and CSAT, support focuses on First Contact Resolution rates.
• Industry relevance varies significantly - customer service applies universally across all sectors, while customer support primarily serves IT, SaaS, and technology companies.
• The financial impact is substantial - emotionally connected customers provide 306% higher lifetime value, while improving First Contact Resolution by 10% can reduce churn by 30%.
When businesses properly structure teams around these distinctions, they create comprehensive experiences that address both technical reliability and emotional connection, leading to stronger customer loyalty and sustainable growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
MORE LIKE THIS

Customer service vs. customer support: A complete breakdown

Customer service vs customer experience: The essential differences you need to know

Customer service vs customer experience: The essential differences you need to know
Support made easy. So your team can breathe.