Set up AI agents for customer support in less than 10 minutes
Set up AI agents in minutes
AI Agents vs chatbots explained: Everything you need to know
Sneha Arunachalam .
Nov 2025 .

Most businesses still think “AI agent” is just a fancy name for a chatbot.
That misunderstanding is costing them customers, time, and money.
Here’s the truth: your chatbot might reply fast, but your AI agent can think. One follows scripts — the other solves problems. And as customer expectations explode, that difference determines whether you deliver delight or frustration.
In this blog, we’ll break down the real difference between AI agents and chatbots, why it matters more than ever, and how choosing the right one could 10x your customer satisfaction.
What is a chatbot and how does it work?
You've probably chatted with one already today. Chatbots are everywhere now, those little chat windows that pop up on websites, the automated helpers in messaging apps.
They're computer programs designed to have conversations with people through text or voice.
The goal?
Make talking to a machine feel like talking to a human. Sometimes it works. Sometimes... not so much.
Scripted workflows and decision trees
Think of traditional chatbots like those old "choose your own adventure" books.
Every conversation follows a predetermined path with specific responses mapped out in advance.
Here's how it actually works: chatbots use decision trees to navigate conversations. Each time you respond, the bot checks its internal flowchart and picks the next appropriate reply. It's basically an "if this, then that" system.
Ask about store hours?
The bot recognizes those keywords and serves up the pre-written answer. Simple enough.
Most chatbots fall into two categories:
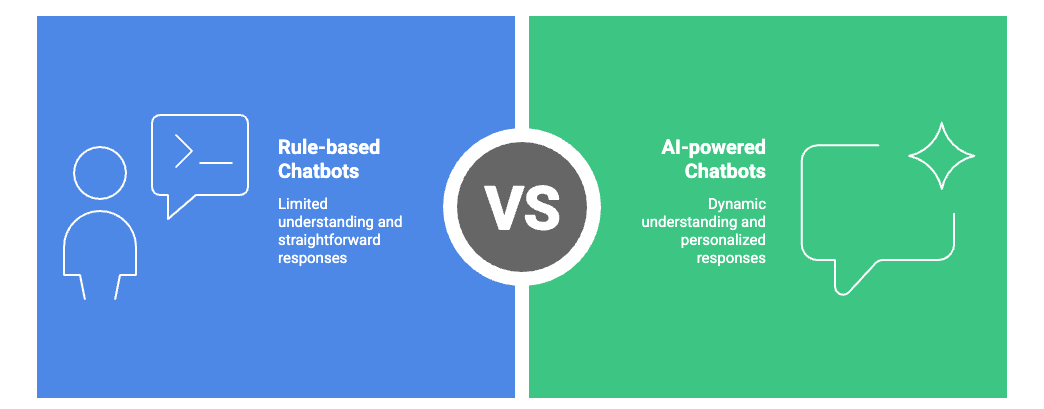
- Rule-based chatbots: These stick to the script. They follow predetermined rules and work great for repetitive questions. Think FAQ bots that can handle the same queries over and over.
- AI-powered chatbots: A step up from basic rule-followers, these use natural language processing to better understand what you're asking. They're smarter but still limited by their programming.
Common chatbot use cases
You'll typically see them:
- Answering the same questions customers ask every day
- Tracking orders and booking appointments
- Collecting contact info from potential customers
- Walking people through basic troubleshooting
- Pointing users to helpful articles
- Processing straightforward returns
- Gathering feedback through structured surveys
They're workhorses for 24/7 support. Your customers get instant answers even when your team is sleeping.
Limitations of traditional chatbots
But here's where things get messy. 48% of people say their chatbot experiences fail to solve actual problems or miss the point entirely. Another 38% find them frustrating to manage because they don't learn on their own.
The problems are real:
- They miss the point: Most chatbots still don’t truly understand what customers are asking. Throw in a bit of slang or a casual tone, and they get confused fast.
- Wrong answers: Instead of solving the problem, they often deliver unhelpful or irrelevant responses because they lack context.
- Language struggles: They’re built to match keywords, not to understand natural human conversation, which makes interactions feel robotic.
- No memory: Traditional bots can’t learn from past mistakes. Every new situation has to be manually programmed, making them rigid and slow to improve.
The bottom line? 72% of people feel chatbots waste their time during customer service. That's a problem when you're trying to build trust and solve real issues.
This gap between what chatbots can do and what customers need is exactly why AI agents entered the picture.
This is exactly where many support teams get stuck. They add more chatbot flows, more rules, and more fallbacks — but the experience doesn’t improve.
AI-first platforms like SparrowDesk approach this differently.
Instead of expanding scripts, SparrowDesk’s AI Agents are designed to reason through customer issues, retain context, and take real actions across your support stack without forcing customers into rigid paths.
Watch how AI agents resolve real support problems
What is an AI agent and how is it different?
Now we're talking about something completely different.
AI agents aren't just fancy chatbots, they're a whole new category of technology that autonomously performs tasks by designing workflows with available tools. We're talking about systems that actually think and act, not just respond.
Autonomous decision-making
Think of it like this: chatbots are like automated receptionists following a script. AI agents? They're more like skilled employees who can figure things out on their own.
The real difference comes down to autonomy. AI agents make decisions without someone holding their hand every step of the way.
A contact center AI agent doesn't just spit out canned responses. It can:
- Ask follow-up questions that actually make sense for your specific problem
- Dig through company knowledge bases to find real solutions
- Decide whether it can handle your issue or if you need a human
That's not following a flowchart — that's problem-solving. Instead of "if this, then that" logic, AI agents look at your situation, consider past experiences, and figure out what to do next.
Use of large language models (LLMs)
Here's where things get interesting. AI agents run on large language models that give them something chatbots just don't have — the ability to actually understand and reason.
This means they can:
- Handle text, voice, video, and code all at once
- Keep track of what you're talking about throughout the conversation
- Make decisions based on evidence, not just keywords
A chatbot matches your words to preset responses. An AI agent breaks down complex problems into smaller pieces, tackles each part, and coordinates everything together. It's like having a digital assistant that can juggle multiple tasks while remembering what you discussed last week.
Real-time learning and adaptation
Let's be honest — this is where AI agents really shine. They get smarter with every interaction.
Here's how that works:
- Memory structures - They remember your preferences and past conversations
- Feedback loops - When you tell them something didn't work, they adjust
- Iterative refinement - They store info about mistakes so they don't repeat them
AI agents adapt to new situations without needing a programmer to update their code. Through reinforcement learning, they basically grade themselves on how well they're doing and improve accordingly.
The numbers back this up. McKinsey research shows organizations using AI-enabled customer service agents increased issue resolution by 14% per hour and reduced handling time by 9%.
Take logistics — an AI agent can optimize delivery routes by juggling speed, cost, and fuel efficiency simultaneously. That's not something you program once and forget. That's ongoing problem-solving that gets better over time.
In modern support environments, this kind of learning isn’t optional, it’s essential.
SparrowDesk’s AI Agents continuously improve by learning from resolved conversations, agent feedback, and customer behavior.
That means fewer repeated mistakes, smarter resolutions, and AI that gets better the more it’s used without constant manual retraining.
Build support that gets smarter over time
AI agent vs chatbot: key differences explained
The real differences hit you once you see these technologies in action. Chatbots respond — AI agents think. Chatbots talk — AI agents get stuff done.
Let's break down what actually separates them.
1. Interaction complexity
Ever tried having a real conversation with a chatbot? It's like talking to someone reading from a script.
AI agents handle complex conversations that actually flow naturally. They get context, follow along when topics shift, and respond like a human would. Meanwhile, chatbots — even the fancy AI-powered ones — stick to simpler interactions. They might catch some context, but ask them something that wasn't in their training and you'll hit a wall.
Here's how one expert puts it: "A conversation with an AI agent feels like talking to an intelligent customer service representative, whereas a chatbot conversation feels like choosing preset responses from a menu".
That's the difference right there.
2. Task execution and autonomy
Think of it like this: chatbots are handed a playbook and told to follow it. AI agents write their own playbook as they go.
AI agents can:
- Dig through complex data on their own
- Make decisions without checking with anyone
- Change their approach mid-task
- Run completely independently
Regular chatbots? They pull answers from their knowledge base and call it a day. No reasoning, no analysis.
3. Learning and adaptability
This one's huge. AI agents get smarter with every interaction — they remember past conversations, learn from feedback, and store solutions for next time.
Most chatbots don't learn anything. Each conversation starts from scratch. In fact, 38% of users say chatbots don't self-learn, which means every mistake gets repeated over and over.
AI agents evolve. Chatbots stay stuck.
4. Integration with external tools
AI agents connect to everything — your CRM, payment systems, scheduling tools, you name it. They pull data in real-time, trigger workflows, and handle complex multi-step processes without breaking a sweat.
Chatbots typically connect to one or two basic systems for simple data lookups. Want them to do something new? Someone's got to manually wire it up.
5. Personalization and context awareness
Here's where the difference becomes obvious. AI agents analyze your customer data, remember previous interactions, and predict what someone might need next.
Chatbots might use your name and remember what you said five minutes ago. That's about it. AI agents build actual understanding over time, making every interaction feel genuinely personal rather than robotic.
That’s the real power SparrowDesk’s AI Agents bring to customer support.
Instead of surface-level personalization that only reuses a name, SparrowDesk’s AI Agents analyze customer history, past tickets, preferences, and interaction patterns and then use that context to resolve issues more intelligently.
In real customer service environments, this translates to measurable results: teams using SparrowDesk’s AI Agents consistently see higher resolution rates, fewer escalations, and faster ticket turnaround because the AI isn’t just replying, it’s reasoning.
See SparrowDesk AI Agents in action →
When to use a chatbot vs an AI agent
Let's be honest — there's no magic formula here. Your specific situation should drive this choice, not what everyone else is doing.
Customer-facing vs employee-facing scenarios
Think of it like this: customer-facing interactions often need a mix of both technologies. Chatbots handle the predictable stuff — FAQs, basic transactions, routine inquiries. AI agents step in when things get complicated.
One expert puts it perfectly: "For primarily customer-facing scenarios, I think there will be a mix of traditional chatbots and modern generative AI agents. For employee-facing scenarios, an agent is more favorable".
Inside your organization? AI agents usually win. They're built for the messy, interconnected work that happens behind the scenes:
- HR processes that span multiple systems
- Complex internal workflows with lots of moving parts
- Data analysis that requires actual decision-making
The reason is simple — internal processes are rarely straightforward. They involve multiple systems and way more complexity than "What are your store hours?"
Simple vs complex workflows
Here's where it gets clear-cut. Chatbots work great for:
- Pulling answers straight from your knowledge base
- Booking appointments or tracking orders
- Collecting basic info from users
- Walking people through step-by-step processes
AI agents become essential when you're dealing with:
- Workflows that jump between different systems
- Real-time analysis and decision-making
- Personalized recommendations based on user history
- Situations that need continuous improvement
As one expert notes, "AI agents can understand context, personalize interactions, learn over time, and complete multi-step tasks across applications".
Budget and resource considerations
Money talks, and chatbots speak its language. They cost less upfront and need fewer resources to run.
Basic chatbots start around $7-15 monthly. AI solutions like SparrowDesk’s AI Agents start at $16 per seat and $0.70 per resolved query.Enterprise AI agent platforms can hit $2,000+ monthly.
But here's what matters more — the long-term payoff. AI agents deliver returns through:
- Less human intervention needed
- Higher resolution rates without escalation
- Better customer satisfaction scores
The upfront investment in AI agents usually pays off through their enhanced capabilities and ability to work independently.
Quick decision guide: Should you use a chatbot or an AI agent?
Choosing between a chatbot and an AI agent isn’t about which technology is “better.” It’s about what kind of problems you need to solve and how complex your customer interactions really are.
Use a chatbot if:
Your support mostly involves predictable, repetitive questions (FAQs, store hours, order status).
You want instant replies without deep personalization.
Your workflows are simple and linear, with no decision-making required.
You’re looking for a low-cost, low-maintenance way to offer 24/7 availability.
Escalating complex issues to human agents is acceptable.
Chatbots are ideal for handling volume efficiently, but they rely on predefined scripts and struggle once conversations go off track.
Use an AI agent if:
Customer issues require reasoning, judgment, or multi-step problem-solving.
You need personalized responses based on user history, preferences, or account data.
Your workflows span multiple systems like CRMs, billing tools, or internal databases.
You want the system to learn and improve over time without constant manual updates.
Reducing handoffs and resolving issues end-to-end is a priority.
AI agents are built for autonomy. They don’t just respond, they understand, decide, and act.
Use both if you want scale and high CSAT:
Most modern support teams don’t choose one or the other — they combine both.
- Chatbots handle high-volume, low-complexity requests instantly.
- AI agents step in for complex, high-impact issues that require context and action.
- Human agents focus on edge cases, emotional situations, and relationship-building.
This hybrid approach delivers:
- Faster first response times
- Higher resolution rates
- Lower agent workload
- Better overall customer satisfaction
Teams that choose both often look for a platform where chatbots and AI agents aren’t bolted together as add-ons.
SparrowDesk is designed as an AI-first help desk, where automation, AI agents, and human support work together in a single system, rather than competing with each other.
The Helpdesk your team truly deserves.
Bottom line
If your goal is speed alone, a chatbot may be enough.
If your goal is resolution, personalization, and long-term efficiency, AI agents are the better fit.
If you’re scaling support without compromising experience, using both is often the smartest choice.
Implementation and maintenance: what to expect
Let's be honest, setting up these technologies isn't the same experience. The difference between getting a chatbot running versus deploying an AI agent? Night and day.
Training and setup time
Think of it like this: traditional chatbots are like training a new employee who needs explicit instructions for everything. They demand significant upfront work — hundreds of conversation examples, extensive rule configurations, and detailed decision trees.
AI agents? They're more like hiring someone who already knows how to think. Thanks to their built-in smarts, some platforms let you launch a working agent within an hour just by uploading your help docs or connecting your knowledge base. Need to add scheduling or ticket creation? A few clicks and you're done.
That setup time difference can make or break your timeline.
Ongoing updates and feedback loops
Here's where the maintenance story gets interesting. Chatbots need constant hand-holding — regular manual updates, rule tweaks, and ongoing time investment to stay effective.
AI agents keep getting smarter on their own through:
- Learning from every interaction
- User feedback that actually sticks
- Self-improvement without you lifting a finger
This means your AI agent adapts to new situations independently. Most platforms now give you dashboards to track how things are going and spot areas for improvement.
No-code vs manual scripting
The good news?
You don't need to be a programmer anymore. Even traditional chatbot platforms have moved toward visual, drag-and-drop interfaces. Non-technical teams can build working solutions without touching a single line of code.
One of the biggest barriers to adopting AI agents is the belief that setup will be complex or resource-heavy.
Platforms like SparrowDesk reduce that friction by allowing teams to launch AI Agents quickly using existing help docs, workflows, and integrations without writing code or rebuilding processes from scratch.
Get started without heavy setup →
Are AI agents replacing chatbots?
Short answer: no, and that’s not the goal.
AI agents aren’t here to replace chatbots. They’re here to solve the problems chatbots were never designed to handle in the first place.
Chatbots were built for speed and scale. They follow predefined scripts, handle repetitive questions, and keep support available 24/7. For predictable interactions like FAQs, order tracking, or appointment booking, chatbots still do their job well.
AI agents, on the other hand, were created to handle complexity.
They reason through problems, retain context across conversations, make autonomous decisions, and complete multi-step tasks across systems. That’s not an upgrade to a chatbot, it’s a different category altogether.
This is why the “replacement” narrative misses the point.
Evolution, not extinction
What we’re seeing is an evolution in how support systems are designed:
- Chatbots continue to handle high-volume, low-complexity requests efficiently
- AI agents step in when conversations require judgment, personalization, or workflow execution
- Human agents focus on edge cases, emotional situations, and relationship-driven interactions
Each plays a distinct role. Removing chatbots entirely would actually slow teams down and increase costs.
Why hybrid models are becoming the default
Most modern support teams now use a hybrid approach, where chatbots and AI agents work together instead of competing.
In this setup:
- Chatbots filter and resolve simple requests instantly
- AI agents take over when issues become multi-step or context-heavy
- Customers experience faster resolutions without unnecessary handoffs
This layered model is more scalable, more cost-effective, and better aligned with rising customer expectations.
The real shift businesses should focus on
The real question isn’t “Will AI agents replace chatbots?”
It’s “Which problems should each technology handle?”
Chatbots remain valuable for speed and availability. AI agents expand what automation can actually achieve.
Together, they move support from scripted responses toward real problem-solving without breaking what already works.
AI agents vs chatbots in customer support
Customer support is where the difference between chatbots and AI agents becomes impossible to ignore. On paper, both can “handle conversations.” In reality, only one can consistently resolve issues end to end.
Where chatbots struggle in real support scenarios
Chatbots work best when customer requests are predictable. But modern support conversations rarely are.
In real customer support environments, chatbots often fail when:
- Issues require context from past interactions or account history
- A single request turns into a multi-step problem
- Customers phrase questions in unexpected or emotional ways
- Resolution depends on actions across multiple systems (billing, CRM, product data)
When a chatbot hits these limits, it escalates. That handoff adds friction — customers repeat themselves, agents lose time, and resolution slows down.
This is why many teams see high chatbot deflection but low first-contact resolution.
How AI agents change the support equation
AI agents are designed specifically for these complex support moments.
Instead of stopping at answers, an AI agent can:
- Understand the customer’s intent, even when the request isn’t clearly phrased
- Pull relevant context from past tickets, account data, and conversations
- Decide whether it can resolve the issue autonomously or involve a human
- Execute actions like updating records, triggering workflows, or applying policies
In customer support, this autonomy matters. It’s the difference between responding to a problem and solving it.
Fewer escalations, fewer handoffs, better outcomes
One of the biggest advantages of AI agents in customer support is their impact on escalations.
Because AI agents can reason through problems and take action, they:
- Resolve more issues without human intervention
- Reduce unnecessary handoffs between bots and agents
- Shorten resolution times for complex tickets
- Preserve context when human agents do step in
The result is a smoother experience for customers and less cognitive load for support teams.
Where chatbots still fit in customer support
This doesn’t mean chatbots are obsolete. In fact, they still play an important role.
Chatbots remain effective for:
- FAQs and knowledge base lookups
- Order tracking and appointment scheduling
- Simple status updates and form-based interactions
- High-volume, low-complexity inquiries
Used correctly, chatbots act as the first line of support, handling volume efficiently and keeping queues clear.
The modern support model: layered, not replaced
The most effective customer support teams don’t choose between chatbots and AI agents, they layer them.
- Chatbots handle the predictable questions at scale
- AI agents take over when conversations require reasoning, personalization, or action
- Human agents focus on edge cases, emotional conversations, and high-value interactions
This layered approach is why modern AI-first help desks like SparrowDesk are designed around agents that can think and act, not just reply. It’s also why teams adopting AI agents see fewer escalations and more consistent resolution without increasing headcount.
This layered support model is exactly how SparrowDesk is built.
SparrowDesk combines chat-based automation for simple requests with AI Agents that can understand intent, pull context from past tickets, and complete multi-step actions across tools.
The result is fewer escalations, faster resolutions, and support teams that can scale without adding headcount.
View SparrowDesk for customer support →
Conclusion
This isn't really about picking sides between AI agents and chatbots. It's about matching the right tool to your actual needs.
Chatbots work great for the basics. They handle simple questions, process straightforward requests, and keep your support running 24/7 without breaking the bank. When your customers need quick answers to common problems, chatbots get the job done.
AI agents? They're built for the complex stuff. They remember past conversations, make smart decisions on their own, and connect all your systems together. Sure, they cost more upfront, but they often pay for themselves through better customer experiences and fewer escalations.
The lines keep blurring as both technologies get smarter. But the core difference stays the same, chatbots follow the script, AI agents write their own. That affects everything your customers experience.
Your choice comes down to three things: how complex your workflows are, what you can spend, and whether you're serving customers or employees.
Most companies we see do best with both — chatbots for the easy stuff, AI agents for everything else.
That’s exactly why modern support teams are moving toward AI-first help desks like SparrowDesk.
Instead of forcing you to choose between chatbots or AI agents, SparrowDesk brings both together in a single system, so simple questions are handled instantly, complex issues are resolved intelligently, and human agents step in only when it truly matters.
See how SparrowDesk brings it all together →
Either way, you're aiming for the same goal: giving people the help they need, when they need it. And as this technology keeps getting better, both options will only get more powerful for businesses ready to use them right.
AI agent vs chatbot: Comprehensive comparison table
Core capabilities comparison
Feature | Chatbot | AI Agent |
Intelligence Level | Rule-based or basic AI with predetermined responses | Advanced LLM-powered with reasoning capabilities |
Decision Making | Follows scripted workflows and decision trees | Autonomous decision-making without constant guidance |
Conversation Style | Menu-like, preset responses | Natural, context-aware conversations |
Learning Ability | Limited or no self-learning | Continuous learning from every interaction |
Task Complexity | Simple, single-step tasks | Complex, multi-step workflows across systems |
Autonomy | Requires predefined rules for every scenario | Works independently and adapts to new situations |
Operational differences
Aspect | Chatbot | AI Agent |
Problem Solving | Keyword matching and preset answers | Analyzes, reasons, and develops solutions |
Context Retention | Limited short-term memory | Remembers preferences and past conversations |
Adaptability | Requires manual updates for changes | Adjusts approach in real-time |
System Integration | 1-2 basic system connections | Multiple systems with real-time data access |
Personalization | Basic (name recognition, recent context) | Deep (analyzes history, predicts needs) |
Handling Exceptions | Fails or escalates when off-script | Figures out solutions independently |
Implementation & cost
Factor | Chatbot | AI Agent |
Initial Setup | Hours to days (extensive rule configuration) | Can launch within 1 hour with knowledge base |
Training Required | Hundreds of conversation examples needed | Built-in intelligence, minimal training |
Pricing | $7-15/month for basic solutions | Starting at $16/seat + $0.70/resolved query |
Enterprise Cost | Lower upfront investment | $2,000+/month for advanced platforms |
Maintenance | Constant manual updates required | Self-improving with minimal intervention |
Technical Skills | No-code options available | No-code options available |
Best use cases
Scenario Type | Chatbot | AI Agent |
Customer FAQs | Excellent | Excellent (but may be overkill) |
Order Tracking | Excellent | Excellent |
Appointment Booking | Excellent | Excellent |
Complex Problem Solving | Limited/Fails | Excellent |
Multi-System Tasks | Not capable | Excellent |
Personalized Recommendations | Basic at best | Excellent |
Internal Employee Support | Limited effectiveness | Highly effective |
Real-Time Analysis | Not capable | Excellent |
Continuous Improvement | Requires manual work | Automatic |
Customer experience impact
Experience Factor | Chatbot | AI Agent |
Conversation Feel | "Choosing from a menu" | "Talking to an intelligent representative" |
Understanding | Struggles with slang/casual tone | Natural language comprehension |
Flexibility | Rigid, stuck to script | Adaptable to situation |
Trust Building | Often undermines trust | Builds confidence through competence |
AI agent vs chatbot: Understanding the critical differences for your business
Confused about AI Agent vs Chatbot technologies? You're not alone. Most businesses still can't tell these tools apart—and it's costing them in customer experience and efficiency. This comprehensive guide cuts through the confusion to explain what each technology actually does, when to use which, and why choosing the wrong one could hurt your support operations. Understanding these differences is essential for delivering the fast, personalized service modern customers demand.
- Chatbots follow scripts with predetermined responses and decision trees, making them perfect for routine FAQs and simple repetitive tasks
- AI agents think independently, making autonomous decisions and solving complex problems without constant guidance or programming updates
- Learning capabilities differ drastically—chatbots remain static requiring manual updates while AI agents continuously improve from every interaction
- Integration depth matters significantly—chatbots connect to limited systems while AI agents orchestrate sophisticated workflows across multiple platforms
- Implementation varies widely—chatbots need extensive manual configuration; AI agents can launch quickly using existing knowledge bases
The AI Agent vs Chatbot debate isn't about picking sides—it's about strategic deployment. Chatbots excel at high-volume, predictable customer inquiries and keep costs manageable. AI agents shine with complexity, deep personalization, and multi-step problem-solving. Most successful businesses use both strategically, letting chatbots handle straightforward queries while AI agents tackle everything requiring genuine intelligence and adaptive reasoning.
Frequently Asked Questions
MORE LIKE THIS
Support made easy. So your team can breathe.